CBSE 12th Maths Case Study Questions: CBSE Class 12 is a crucial academic year in a student’s life. The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has been continuously evolving its assessment methods with a focus on application-based and competency-driven learning. One big change in recent years is the inclusion of Case Study Questions in board exams, in all subjects. CBSE Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions assess a student's ability to apply mathematical concepts in real-life contexts, going beyond just formulas and theorems. In the 2025 CBSE Class 12 Mathematics exam, these questions continue to play an important role in evaluating analytical thinking and problem-solving skills. This article will guide you through the format, types, examples, and best preparation strategies for Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions. It also helps in understanding concepts clearly, preparing smartly for exams, and reducing stress.
Also check,
What are CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Case Study Questions?
Case Study Questions in CBSE Class 12 Mathematics aren’t just about theory or calculation. They aim to bridge the gap between classroom learning and real-life applications. With CBSE's push towards competency-based assessment, such questions will likely become even more significant in future exams.
Case Study Questions are a type of competency-based question designed to test a student’s ability to:
- Apply mathematical concepts in real-life situations
- Analyse the given information or data
- Solve problems based on application and reasoning
Instead of direct numerical problems, these questions come with a short passage, situation, or case, followed by 4–5 objective or subjective questions related to that case.
Also Check,
How Many Case Study Questions Are Asked in Class 12 Maths Paper?
According to the CBSE Class 12 Maths Paper Design 2025, the paper includes:
- 3 Case study-based questions, carrying 4 marks each.
- All case study based questions asked in the Section E of the question paper
- Two case study questions have three sub parts (i), (ii), (iii) of marks 1, 1, 2 respectively with some internal choice.
- The third case study question has two sub parts of 2 marks each
These questions require students to understand the given case, extract relevant information, and solve accordingly.
Also Check,
|
How to Get More Than 90% Marks in CBSE 12 Board Exam, Subject-wise Study Plan & Preparation Strategy |
| CBSE 12th Maths Previous Year Question Paper, Download Board Paper PDF With Solutions |
What Are the Important Chapters for Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions?
CBSE tends to pick case-based questions from chapters that lend themselves to real-world applications. Chapters from Which Class 12 Case Study Questions are commonly asked are listed below:
- Applications of Derivatives: Motion, rate of change
- Probability: Daily life chances, events, games
- Matrices and Determinants: Business data, coding/decoding
- Linear Programming: Real-life constraints and optimization
- Vectors and 3D Geometry: Navigation, architecture
- Integrals and Area under Curves: Geometry-based applications
Also check,
| CBSE 12th Chemistry Assertion and Reason Questions with Answers, Important Questions for Board Exam |
| CBSE 12th Biology Assertion and Reason Questions with Answers, Important Questions for Board Exam |
How to Solve Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions Effectively?
To solve Maths case study questions effectively, first read the question carefully and understand the real-life situation given. Identify the maths concepts or formulas needed to solve it. Break the problem into small parts and solve step by step. Practice similar questions regularly to improve speed and accuracy. Here are some expert tips for solving Class 12th Maths Case Study Questions effectively:
1. Understand the Case Thoroughly: Read the passage/case carefully and note down all given numerical values, shapes, dimensions, or relationships.
2. Identify the Chapter and Concept: Try to match the case with the most relevant concept or formula from the syllabus. For example, a motion-based question might relate to derivatives.
3. Break Down the Problem: Treat each sub-question individually. Don’t get overwhelmed by the case’s length, they are often easier than they look!
4. Draw Diagrams or Sketches: A visual approach helps when dealing with geometry, vectors, or calculus. It helps make sense of the situation better.
5. Practice from Sample Papers and Past Year Papers: Use the CBSE Sample Paper 2025 and previous years’ board papers to practice similar case-based questions.
CBSE Class 12 Maths Case Study Question
Let’s look at an example to understand how these questions appear:
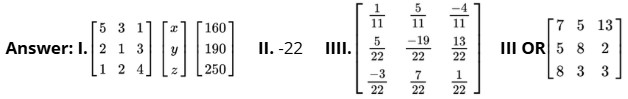
Case.1: Gautam buys 5 pens, 3 bags and 1 instrument box and pays a sum of ₹160. From the same shop, Vikram buys 2 pens, 1 bag and 3 instrument boxes and pays a sum of ₹190. Also Ankur buys 1 pen, 2 bags and 4 instrument boxes and pays a sum of ₹ 250.
Based on the above information, answer the following questions:
(I) Convert the given above situation into a matrix equation of the form AX = B.
(II) Find |A|.
(III) Find A^–1.
OR
(III) Determine P = A^2 – 5A.
Case.2: An organization conducted bike race under two different categories - Boys and Girls. There were 28 participants in all. Among all of them, finally three from category 1 and two from category 2 were selected for the final race. Ravi forms two sets B and G with these participants for his college project. Let B = {b1, b2, b3} and G = {g1, g2}, where B represents the set of Boys selected and G the set of Girls selected for the final race.
Based on the above information, answer the following questions
(I) How many relations are possible from B to G ?
(II) Among all the possible relations from B to G, how many functions can be formed from B to G ?
(III) Let R : B → B be defined by R = {(x, y) : x and y are students of the same gender}. Check if R is an equivalence relation.
OR
(III) A function f : B → G be defined by f = {b1, g1). (b2, g2), (b3, g1)}. Check if f is bijective. Justify your answer.
Answer: (I) 64, (II) 8, (III) Yes, R is an equivalence relation, OR (III) f is a surjective function.
Case.3: Rashmi has to buy some medicines for her grandmother for which she needs to go to a chemist store but she is short of cash with her at home so she decided to first go to the ATM to withdraw some money on the way and then after that visit to the chemist store to buy the medicines. The condition is considered on the three-dimensional cartesian plane such that the points A(3, 2, 1), B(1, −1, 2) and C(−2, 1, 1) represent the position of the house, ATM, and chemist store respectively.
Based on the above information, answer the following questions:
(a) What is the vector joining the points A and B such that the position vector is directed from ATM to Rashmi's house?
(b) What is the magnitude of the vector joining the points A and C such that the position vector is directed from ATM to Chemist store?
(c) What is the scalar product of the vectors and ?
(d) Find the vector product of and .
Answer: (a) 2i + 3j -k, (b) root 26, (c) -13, (d) -i + 5j + 13k
Case.4: Three people A, B and C are playing a game of Ludo at home during the national lockdown due to the pandemic situation of Covid-19. While rolling the dice, B observed and noted the possible outcomes of the throw every time belongs to set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. Let X be the set of players while Y be the set of all possible outcomes. Then, X = {A, B, C} and Y = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}.
Based on the above information, answer the following question:
(i) What is the number of relations from X to Y?
(a) 2^8
(b) 2^9
(c) 2^16
(d) 2^18
Answer: (d) 2^18
(ii) If R : Y → Y be a relation defined as R = {(x, y) : y is double of x}, then which of the following is true regarding the relation R?
(a) Reflexive only
(b) Reflexive and transitive but not symmetric
(c) Reflexive and symmetric but not transitive
(d) Not reflexive, symmetric or transitive
Answer: (d) Not reflexive, symmetric or transitive
(iii) Let R : X → X be defined by R = {(x, y) : x and y have same age}. Then, relation R is ____________________.
(a) an equivalence relation
(b) reflexive only
(c) reflexive and symmetric but not transitive
(d) not reflexive but symmetric and transitive
Answer: (a) an equivalence relation
(iv) Person A wants to know the number of functions from X to Y. How many number of functions are possible?
(a) 64
(b) 216
(c) 729
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) 216
(v) Let R : X → Y, R = {(A, 2), (C, 4), (B, 3), (A, 1), (B, 5)}, then R is _________________.
(a) neither one-one nor onto
(b) one-one but not onto
(c) onto but not one-one
(d) not a function
Answer: (d) not a function
CBSE Class 12 Maths Case Study Question PDF [Free]
Click on the link provided below to download the CBSE Class 12 Maths Case Study Question PDF with answers for free without any login. Get the direct link to download the PDF.
| CBSE Class 12 Maths Case Study Question PDF | Download here |
| CBSE Class 12 Maths Case Study Question- Solution PDF | Download here |
Common Mistakes to Avoid In Maths Case Study Questions
- Skipping the passage: Students often directly jump to the question without understanding the context.
- Misinterpreting the case: Especially in word problems involving diagrams or figures.
- Not revising key formulas: Weak formula recall can ruin your answer.
- Lack of practice: These questions are relatively new, and many students aren’t used to them yet.
Importance of Case Study Questions in Class 12 Maths
Case study questions in Class 12 Maths are important because they test how well students can apply maths in real-life situations. These questions help improve logical thinking and problem-solving skills. They also make learning more practical and useful beyond just memorizing formulas. Practicing them can help students score better in the board exam.
- Encourage real-world connection of abstract concepts
- Enhance logical and analytical thinking
- Strengthen problem-solving approach
- Help students understand the utility of math in daily life
- Increase the weightage of application-based learning in exams
CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus 2025-26
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has released the Maths Syllabus for Class 12 Science, Commerce, and Humanities (Arts) streams for the 2025-26 academic year. This Maths Syllabus outlines the course structure, chapters, and topics that students will need to study in the subject. The CBSE Class 12 Maths syllabus covers a wide range of topics including Calculus, Algebra, Vectors, 3D Geometry, Probability, and Linear Programming. It is divided into units with specific weightage, helping students plan their preparation effectively. The unite-wise chapters and weightage is provided below :
| Unit | Chapter | Weightage |
|
Relations and Functions |
1. Relations and Functions |
8 |
| 2. Inverse Trigonometric Functions | ||
|
Algebra |
3. Matrices |
10 |
| 4. Determinants | ||
|
Calculus |
5. Continuity and Differentiability |
35 |
| 6. Applications of Derivatives | ||
| 7. Integrals | ||
| 8. Applications of Integrals | ||
| 9. Differential Equations | ||
|
Vectors and 3D Geometry |
10. Vectors |
14 |
| 11. Three-Dimensional Geometry | ||
| Linear Programming | 12. Linear Programming | 5 |
| Probability | 13. Probability | 8 |
Check the latest and detailed CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus 2025-26; Check Latest Unit-wise Weightage, Download PDF.
CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Exam Pattern 2025-26
CBSE has not yet released the exam pattern and marking scheme for the 2025-26 academic year. Based on the official question paper design shared along with the syllabus, it is likely that the board will follow the same exam pattern and marking scheme as in 2024-25. The CBSE Class 12 Mathematics board exam for 2024–25 consisted of a theory paper of 80 marks and an internal assessment of 20 marks. The question paper was divided into five different sections:
| Section | Question Type | Number of Questions | Marks |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Multiple Choice Questions & Assertion and Reason Questions (1 mark) | 20 | 20 |
| B | Very Short Answer (2 mark) | 5 | 10 |
| C | Short Answer (3 marks) | 6 | 18 |
| D | Long Answer (5 marks) | 4 | 20 |
| E | Case Study-Based Questions (4 marks) | 3 | 12 |
| Total | 38 | 80 | |
Check the latest and detailed CBES Class 12th Maths Exam Pattern 2025-26 with Marking Scheme.