CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus 2025-26: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has released the Maths Syllabus for Class 12 Science, Commerce, and Humanities (Arts) streams for the 2025-26 academic year. This Maths Syllabus outlines the course structure, chapters, and topics that students will need to study in the subject. Additionally, it provides details about the exam pattern and assessment criteria. Mathematics is one of the core subjects for students in the Science and Commerce streams, and plays a crucial role in preparing for competitive exams like JEE, CUET, NDA, and CA Foundation.
A strong foundation in this subject not only ensures excellent board results but also boosts preparation for competitive exams. This resource will be helpful for students to understand the scope of the curriculum and plan their studies accordingly. The CBSE Maths Syllabus is designed to:
- Provide a strong academic foundation.
- Prepare students for national-level competitive exams.
- Encourage conceptual understanding, application, and analysis rather than rote learning.
CBSE 12th Maths Syllabus 2025-26 Download PDF
The CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus is designed to provide students with a well-rounded education that equips them for further studies and competitive exams. A deep understanding of the Maths Syllabus, combined with consistent effort, is essential for achieving success in these assessments. Below, students can get the direct link to download the CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus PDF.
Also Check,
CBSE 12th Maths Case Study Questions 2025-26, Check Important Questions and Tips to Solve
CBSE 12th Maths Syllabus 2025-26 Download PDF
The CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus for 2025–26 is designed to promote conceptual clarity, analytical skills, and real-life problem-solving abilities. Start early, be consistent, and focus on understanding over memorisation. Below, students can check the CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus, including unit-wise weightage and other useful data insights.
Unit I: Relations and Functions
- Relations and Functions: Types of relations: reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto functions.
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions: Definition, range, domain, principal value branch. Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions.
Unit II: Algebra
- Matrices: Types, operations, properties, transpose, symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices
- Determinants: Minors, co-factors and applications of determinants, adjoint and inverse of a square matrix. Consistency, inconsistency and number of solutions of system of linear equations by examples, solving system of linear equations in two or three variables using inverse of a matrix.
Unit III: Calculus
- Continuity and Differentiability: Continuity and differentiability, chain rule, derivative of composite functions, derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions, derivative of implicit functions. Concept of exponential and logarithmic functions. Derivatives of logarithmic and exponential functions. Logarithmic differentiation, derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms. Second-order derivatives.
- Applications of Derivatives: rate of change of quantities, increasing/decreasing functions, maxima and minima
- Integrals: Integration of a variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts, Evaluation of simple integrals, Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (without proof). Basic properties of definite integrals and evaluation of definite integrals.
- Applications of Integrals: Applications in finding the area under simple curves, especially lines, circles/ parabolas/ellipses
- Differential Equations: Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation. Solution of differential equations by method of separation of variables, solutions of homogeneous differential equations of first order and first degree. Solutions of linear differential equation
Unit IV: Vectors and 3D Geometry
- Vectors: Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines and direction ratios of a vector. Types of vectors, position vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a vector, addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Properties and application of scalar product of vectors, vector product of vectors.
- Three-Dimensional Geometry: Direction cosines and direction ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian equation and vector equation of a line, skew lines, shortest distance between two lines. Angle between two lines.
Unit V: Linear Programming
- Introduction, graphical method of solving linear programming problems (only two variables), feasible and infeasible regions, feasible and infeasible solutions, optimal feasible solutions
Unit VI: Probability
- Conditional probability, multiplication theorem on probability, independent events, total probability, Bayes’ theorem.
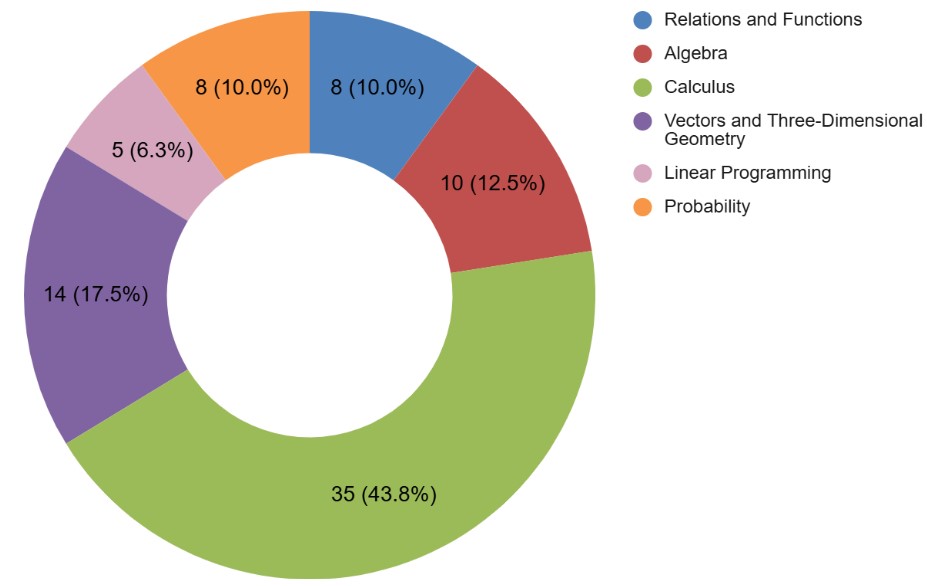
CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Unit-wise Weightage
The CBSE Class 12 Mathematics syllabus is divided into several units, each carrying a specific weightage in the board exam. Understanding the unit-wise weightage helps students prioritise their preparation. The Calculus unit, being the most important, has the highest weightage of 35 marks. Below, we are providing the CBSE 12th Math Unit-wise weightage for your reference. This distribution helps students understand where to focus more time and effort for better results in the final exam.
| Unit No. | Unit Name | Marks |
| I | Relations and Functions | 8 |
| II | Algebra | 10 |
| III | Calculus | 35 |
| IV | Vectors and Three-Dimensional Geometry | 14 |
| V | Linear Programming | 5 |
| VI | Probability | 8 |
| Total | 80 | |
|
Internal Assessment |
20 |
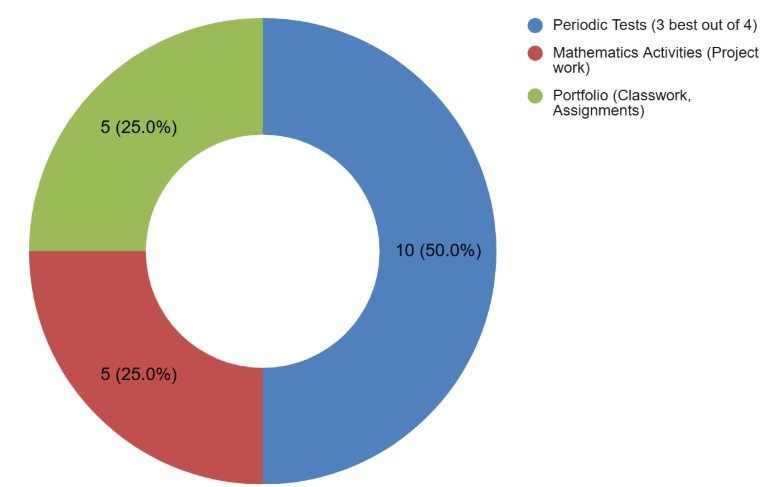
Internal Assessment is further divided into three components, i.e., Periodic Tests, Project work and Portfolio, whose breakup is given below:
| Component | Marks |
| Periodic Tests (3 best out of 4) | 10 |
| Mathematics Activities (Project work) | 5 |
| Portfolio (Classwork, Assignments) | 5 |
| Total | 20 |
Tips for Covering the CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus Effectively
- Understand the Maths Syllabus Thoroughly: Before you begin your preparation, carefully go through the entire Maths Syllabus and marking scheme provided by CBSE. This helps you focus on the most important topics.
- Create a Study Plan: Divide the Maths Syllabus into manageable sections and create a realistic study plan. Allocate time for each subject based on its difficulty level and your comfort.
- Use NCERT Books: CBSE recommends NCERT textbooks for exam preparation, as most of the questions are based on these books. Read the chapters thoroughly and practice the questions at the end.
- Create Revision Notes: Create concise revision notes with essential formulas, concepts, and important points for quick last-minute review.
- Solve Sample Papers and Previous Years Papers: CBSE releases sample question papers every year to help students get familiar with the exam pattern. Solve as many sample papers and previous year's question papers as possible. Also, solve chapter-wise board questions to gain a strong command over each chapter.
- Revise Regularly: Keep revising the concepts regularly, and make sure to cover all the important topics at least two months before the exams.