CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus 2025-26: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has released the Class 10 Science Syllabus for 2025-26. The CBSE 10th Science Syllabus 2025-26 serves as a complete guide for students preparing for the board exam. It highlights the chapters and topics that students need to study in Science. It also explains the exam pattern and how the paper will be designed. Science is a crucial subject for Class 10 students because it lays a strong foundation for higher studies and competitive exams, such as JEE, NEET, NDA, and CUET. By following the updated syllabus, students can better prepare for their board exams and achieve good marks. This article will be helpful for students to understand the scope of the curriculum and plan their Class 10th Board Preparations accordingly. The CBSE Science Syllabus is designed to:
- Provide a strong academic foundation.
- Build a strong foundation for national-level competitive exams.
- Encourage conceptual understanding, application, and analysis rather than rote learning.
CBSE 10th Science Syllabus 2025-26 Download PDF
The CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus aims to build a solid foundation in Science and prepare students for higher education and competitive exams. A clear understanding of the syllabus and consistent study habits are key to scoring well in the board exam. Below, we have provided a direct link for students to download the CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus PDF.
| CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus 2025-26 Download PDF |
CBSE 10th Science Syllabus 2025-26 Download PDF
The CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus for 2025-26 is designed to focus on understanding, application, and analysis instead of rote memorisation. Knowing the complete syllabus in advance helps students feel more confident and organised. Below, students can check the CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus, including unit-wise weightage and other useful data insights.
Unit I: Chemical Substances - Nature and Behaviour
- Chemical Reactions and Equations: Chemical reactions, Chemical equation, Balanced chemical equation, types of chemical reactions: combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, precipitation, endothermic, exothermic reactions, oxidation and reduction.
- Acids, Bases and Salts: Acids and Bases – definitions in terms of furnishing of H+ and OH– ions, identification using indicators, chemical properties, examples and uses, neutralization, concept of pH scale (Definition relating to logarithm not required), importance of pH in everyday life; preparation and uses of Sodium Hydroxide, Bleaching powder, Baking soda, Washing soda and Plaster of Paris.
- Metals and Non-metals: Properties of metals and non-metals; Reactivity series; Formation and properties of ionic compounds; Basic metallurgical processes; Corrosion and its prevention.
- Carbon and its Compounds: Covalent bonds – formation and properties of covalent compounds, Versatile nature of carbon, Hydrocarbons – saturated and unsaturated, Homologous series. Nomenclature of alkanes, alkenes, alkyne and carbon compounds containing functional groups (halogens, alcohol, ketones, aldehydes). Chemical properties of carbon compounds (combustion, oxidation, addition and substitution reactions). Ethanol and Ethanoic acid (only properties and uses), soaps and detergents.
Unit II: World of Living
- Life processes: ‘Living Being’. Basic concept of nutrition, respiration, transport and excretion in plants and animals.
- Control and co-ordination in animals and plants: Tropic movements in plants; Introduction of plant hormones; Control and co-ordination in animals: Nervous system; Voluntary, involuntary and reflex action; Chemical co-ordination: animal hormones.
- Reproduction: Reproduction in animals and plants (asexual and sexual), reproductive health needs and methods of family planning. Safe sex vs HIV/AIDS. Childbearing and women’s health.
- Heredity and Evolution: Heredity; Mendel’s contribution- Laws for inheritance of traits: Sex determination; brief introduction.
Unit III: Natural Phenomena
- Light – Reflection and Refraction: Reflection of light by curved surfaces; Images formed by spherical mirrors, centre of curvature, principal axis, principal focus, focal length, mirror formula (Derivation not required), magnification. Refraction: Laws of refraction, refractive index. Refraction of light by spherical lens; Image formed by spherical lenses; Lens formula (Derivation not required); Magnification. Power of a lens.
- The Human Eye and the Colourful World: Functioning of a lens in the human eye, defects of vision and their corrections, applications of spherical mirrors and lenses. Refraction of light through a prism, dispersion of light, scattering of light, and applications in daily life (excluding the colour of the sun at sunrise and sunset).
Unit IV: Effects of Current
- Electricity: Electric current, potential difference and electric current. Ohm’s law; Resistance, Resistivity, Factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends. Series combination of resistors, parallel combination of resistors and its applications in daily life. Heating effect of electric current and its applications in daily life. Electric power, Interrelation between P, V, I and R.
- Magnetic effects of current: Magnetic field, field lines, field due to a current carrying conductor, field due to current carrying coil or solenoid; Force on current carrying conductor, Fleming’s Left Hand Rule, Direct current. Alternating current: frequency of AC. Advantages of AC over DC. Domestic electric circuits.
Unit V: Natural Resources
- Our Environment: Eco-system, Environmental problems, Ozone depletion, waste production and their solutions. Biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances.
CBSE Class 10 Science Unit-wise Weightage
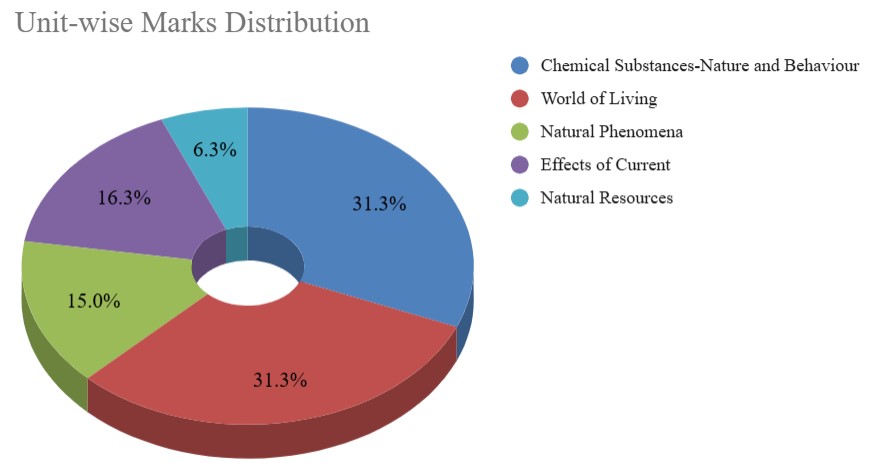
The CBSE Class 10 Science syllabus is divided into five different units, each carrying a specific weightage in the board exam. Understanding the unit-wise weightage helps students prioritise their preparation. The Chemical Substances-Nature and Behaviour and World of Living units are the most important and have the highest weightage of 25 marks. Below, we are providing the CBSE 10th Science Unit-wise weightage for your reference. This distribution helps students understand where to focus more time and effort for better results in the final exam.
| Unit No. | Unit Name | Marks |
| I | Chemical Substances-Nature and Behaviour | 25 |
| II | World of Living | 25 |
| III | Natural Phenomena | 12 |
| IV | Effects of Current | 13 |
| V | Natural Resources | 5 |
| Total | 80 | |
| Internal Assessment | 20 |
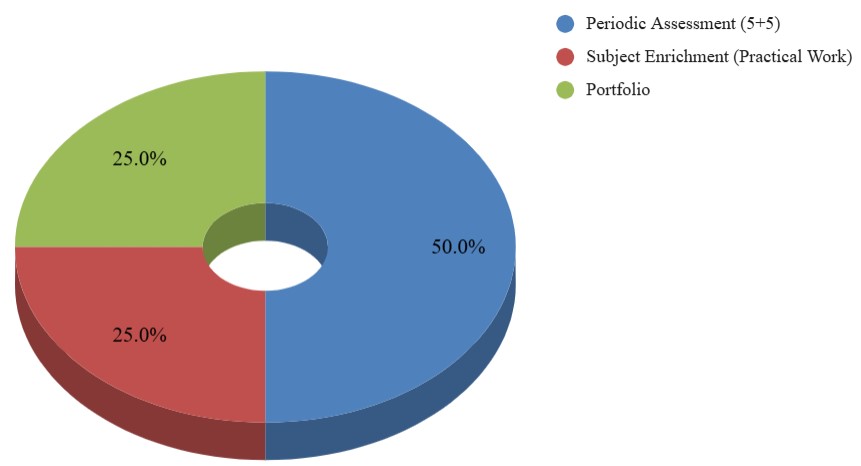
Internal Assessment is further divided into three components, i.e., Periodic Tests, Project work and Portfolio, whose breakup is given below:
| Component | Marks |
| Periodic Assessment (5+5) | 10 |
| Subject Enrichment (Practical Work) | 5 |
| Portfolio | 5 |
| Total | 20 |
How to Cover the CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus Effectively?
Covering the CBSE Class 10 Science syllabus effectively requires smart planning and consistent effort. With a mix of theory, practicals, and application-based questions, Science can feel challenging, but the right approach makes it manageable. Following the syllabus systematically, revising regularly, and focusing on key topics can help students prepare well and score higher in the board exam.
- Understand the Syllabus Thoroughly: Go through each chapter, topic, and marking scheme to plan your study schedule.
- Create a Study Plan: Divide time for Physics, Chemistry, and Biology and stick to a daily or weekly plan and create a realistic study plan. Allocate time for each subject based on its difficulty level and your comfort level.
- Use NCERT Books: CBSE recommends NCERT textbooks for exam preparation, as most of the questions are based on these books. Read the chapters thoroughly and practice the questions at the end.
- Create Revision Notes: Create concise revision notes with important formulas, definitions, diagrams, and reactions for quick last-minute review.
- Focus on Visual Learning: Use Mind maps, flowcharts, and diagrams to make concepts easier to remember.
- Solve Sample Papers and Previous Years Papers: CBSE releases sample question papers every year to help students get familiar with the exam pattern. Solve as many sample papers and previous year's question papers as possible.
- Focus on Practical Subjects: For subjects with practical components, ensure you spend sufficient time in the lab and understand the experiments thoroughly.
- Revise Regularly: Keep revising the concepts regularly, and make sure to cover all the important topics at least two months before the exams.
CBSE Class 10 Science Exam Pattern 2025
CBSE has released the exam pattern and marking scheme for the 2025-26 academic year. Based on the official question paper design shared along with the syllabus, the board will follow the same exam pattern and marking scheme as in 2024-25. The CBSE Class 12 Science board exam for 2025–26 consists of a theory paper of 80 marks and the remaining 20 marks for the practical exam. The question paper will be divided into three sections- Section A (Biology), Section B (Chemistry) and Section C (Physics):
| Section | Question Type | Number of Questions | Marks |
| A |
|
16 | 30 |
| B |
|
13 | 25 |
| C |
|
10 | 25 |
| Total | 39 | 80 | |
Check the latest and detailed CBES Class 10th Science Exam Pattern 2025-26 with Marking Scheme.


